Lesson 8: Designing Learning Environments for Young Children
with Special Needs
Attention
After watching the video, think about your earliest classroom experiences. Did they incorporate universal design principles? How so?
Learning Outcomes
Upon completion of this lesson's material, students will be able to
- Recognize and match the learning design terms to the correct definition.
- Discuss types of supplementary aids or supports within learning environments that may be necessary for young children with delays or disabilities to be successful.
- Identify factors to consider when purchasing classroom materials.
- Describe key characteristics of well-designed indoor and outdoor learning environments for young children with delays or disabilities.
- Describe the types of activity areas or learning centers usually found in learning environments designed for infants, toddlers, preschoolers and children in early primary grades and explain why those activities and/or learning centers are important.
Teaching
The environment is critical to the learning of young children. Teachers serve as environmental engineers as they designed both indoor and outdoor play areas for students to maximize their learning opportunities. It is important that both the instructional materials and the environment support children with a variety of delays and disabilities.
Learning environment consists of its physical attributes (space, room arrangement, equipment), the human dimension (the atmosphere and interactions among individuals), and the curricular environment (content, routines, goals/outcomes).
Classroom ecology refers to the environmental modifications and arrangements of features of classroom environments that can have an impact on learning for young children with delays or disabilities.
Five Principles of Environmental Design for a Learning Environment
- Be organized
- Be capable of creating a caring community
- Have clear goals that reflect particular instructional emphasis,
- Protect health and safety of children and
- Allow all students equal access to age appropriate materials
Key Dimensions to the organization of a learning environment
- Available space and room arrangement
- Age of the children, Population density
- Individual differences of the children
- Aesthetics and visual appeal
- Accessibility, Safety and health
- Materials and equipment
- Organization/scheduling, budget, and Child-adult ratios.
Now that you have read the chapter let's look at a few images of classrooms.
Indoor Learning Environments
Compare image 1 and image 2.
 Image 1
Image 1
 Image 2
Image 2
Now think about the children in your care, the activity areas, the safety of the children, and learning experience for those children. Consider a child with special needs, how would he function in either of the classrooms? Think about a wide variety of diagnosis, does a specific diagnosis make functioning in those classrooms more successful?
Outdoor Learning Environments
Think about the children in your care and the outside playground and consider the safety and learning experience for those children. Now consider a child with special needs, how would he function ineither of these playgrounds? Think about a wide variety of diagnosis, does a specific diagnosis make functioning in those playgrounds more successful?
Take a look at all 3 images below – Which images foster inclusion? Why? Why not?
 Image 1
Image 1
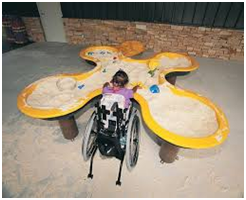 Image 2
Image 2
 Image 3
Image 3
Designing the Learning Environment
- Visual environment - How can we enhance the visual environment for a child with low or no vision?
- Auditory environment - How can we capitalize on the auditory environment for auditory learners?
- Social environment - How can we adapt the social environment for children with impulsive behavior, attention deficits, or behavior problems?
- Individual children - Make use of diverse strengths of the various people on the child's team and respect each child's strengths and needs.
Selecting Learning Materials
This lesson's discussion question allowed you to look at a wide variety of learning materials. Think about the ones you and your classmates purchased. Are there any that stood out to you? Why?
Assessment
Lesson 8 Quiz
- Match the terms to the definition.
Terms Definitions Accessibility Environmental modifications and arrangements of features of classroom environment that can have an impact on learning for young children with delays or disabilities. Activity areas or learning centers A behavioral science concept states that certain behaviors are more likely to occur in the presence of specific stimuli while the behavior is initially being reinforced. Assistive technology Arranging sequencing of activities so that less or low probability are followed by high probability and motivating activities. Augmentative or alternative communication (ACC)Child find Applying good health practices to control the spread of communicable diseases and illnesses: also requires that the cleansing of materials and surfaces with disinfectant become a regular part of an adult's duties in the classroom. Augmentative or alternative communication (ACC) Applying good health practices to control the spread of communicable diseases and illnesses: also requires that the cleansing of materials and surfaces with disinfectant become a regular part of an adult's duties in the classroom. Classroom ecology A sense of helplessness for children when their interactions with the environment prove to be futile or produce inconsistent results or negative feedback.
Environment Any item, piece of equipment, or product system that increases, maintains, or improves functional capabilities of individuals with disabilities. Learned helplessness The quality of the environment that provides the learner with predictable and immediate outcomes from any environmental interaction or immediate and consistent feedback for child interactions.
Premacking Adaptations of the environment aimed at equalizing participation opportunities for persons with disabilities, including adaptations necessary to ensure physical and cognitive access and successful goal attainment by young children with delays or disabilities. Responsivity The sum total of the physical and human qualities that combine to create a space in which children and adults work and play together.
Stimulus-control For children who are non-verbal or have limited verbal abilities, devices or systems that can be used to allow them to respond within learning environments. Universal precautions Organized space within a classroom, typically designed to accommodate small groups of children and a teacher, which are dedicated to activities based on a theme or developmental domain. - Describe (5) key characteristics of well-designed indoor and outdoor learning environments for young children with delays or disabilities.
- List the types of activity areas or learning centers usually found in learning environments designed for infants, toddlers, preschoolers and children in early primary grades. Describe why they are important to consider.
Lesson 8 Discussion
Chapter 7 discusses designing learning environments for young children. Since you have created an infant/toddler/preschool environment in previous classes, I am going to mix things up a bit. In this lesson, instead of …. you will be purchasing materials for your classroom.
Consider this scenario, your program has just received a $ 5,000.00 grant from an anonymous donor. You are able to use that money to purchase classroom supplies, but the donor's stipulation is that the money must be used to purchase materials to enhance your program so it is more assessable to children with special needs. In other words, you must use your funds to purchase items for children who are hearing impaired, visually impaired, have low muscle tone, have rigid muscle tone, are under-stimulated or over-stimulated by materials, and/or demonstrate cognitive delays. (Please consider a child with the same diagnosis as your research paper also.)
Once you have determined how you will spend your money, explain to the class what items you would purchase and why.
Here are a few resources that may be helpful when deciding what to purchase:
discountschoolsupplies.com
learningresources.com
pwap.com
lakeshorelearning.com
communityplaythings.com
mayer-johnson.com
Please share other resources that you know about or run across in your research with the rest of the class.